The Software Testing industry has undergone a massive transformation in the last decades with new opportunities emerging. It’s vital to maintain a software application’s successful efficiency and software testing is necessary to ensure that the application performs without errors. Testing is carried out on the basis of the software development process to ensure that the designed software meets all of the customer’s expectations and preferences. There are numerous testing methods available, each of which varies greatly based on the software and development method.
Software testing, like any other complicated models is divided into phases, each of which is characterized by a distinct set of activities. This article on the Software Testing Life Cycle will give you a thorough understanding of all the phases involved in testing.
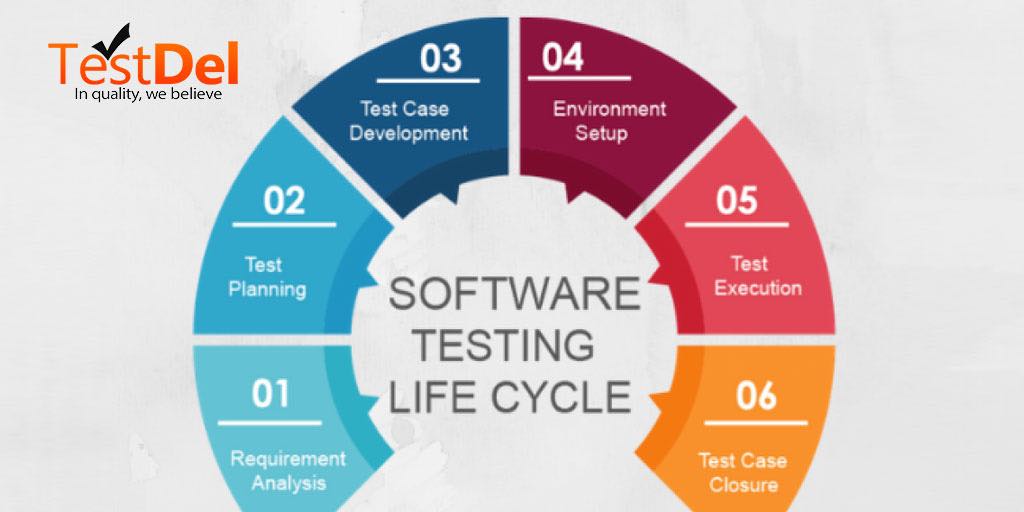
Different stages in Software Testing Life Cycle
Stage 1:- Requirement Analysis
The first phase in the Software Testing Life Cycle is Requirement Analysis. The Quality Assurance (QA) team perceives the demands in terms of what we can assess and determines the verifiable specifications in this phase. During this process, the test team examines the criteria from a testing standpoint in order to determine the specifications that can be tested. To fully comprehend the requirements, the QA team can communicate with various stakeholders such as the customer, management consultant, technical leads, systems engineers and so on.
Stage 2:- Test Plan
The most critical step of the Software Testing Life Cycle is Test Planning, where all testing strategies are established. This stage is also known as the Test Strategy stage. The Testing Team is active in this process to assess the program’s commitment and projected costs. It establishes the project’s goal and framework.
As Test Plan is the most crucial step in the software testing life cycle, the following are the measures required in creating a test plan:
- Assess the product.
- Create a Test Strategy.
- Describe the test goals.
- Specify the test criteria.
- Organizing Resources.
- Construct a Test Environment.
- Approximation and Preparation.
- Choose a Test Deliverable.
Stage 3:- Development of Test Cases
When the test planning process is finished, the test case creation period starts. This is the process of the STLC where the research team takes thorough notes on the test cases. In addition, to test scenarios, the research team develops test data for testing. When the test cases are complete, they are evaluated by group mates or the QA lead. A successful test case is one that finds flaws while still covering the majority of the situations on the device under test. Here’s a step-by-step reference to creating a successful test case:
- Precise and straightforward test cases are needed.
- Create a test case that considers the end consumer.
- Repetition of test cases should be avoided.
- Don’t take your software application’s capabilities and features for granted.
- Ensure that all software requirements are met.
- The test case id should be named in such a way that it can be easily detected when monitoring defects.
- Applying testing methods
- You should restore the Test Environment to its well before condition in the test case you make.
- Every time the test case is run, the same outcomes should be obtained.
- Your collaborators should be able to spot flaws in your test case design.
Stage 4:- Environment
The test environment is the software and/or hardware setup upon which the testing team can run the tests, but if it hasn’t been configured in time when you’re ready to begin, you’ll run into problems. Ascertain that all relevant test data has been entered into the system and is ready for use. Typically, this process occurs concurrently with the development of stages of test cases.
The test environment entails the development of various parts such as:
- Setup of the Test Server – Not all tests can be run on a local computer. It may be necessary to set up a test server capable of supporting applications.
- Network – We must set up the network in accordance with the specifications.
- Setup of Test PCs – We’ll need to set up different browsers for each tester.
- Bug Reporting – Testers should have access to bug tracking software.
- Generating Test Data for the Test Environment – To test software products, many businesses have a different test environment. Copying output data to test is a popular approach.
Stage 5:- Test Execution
Now that the tests are prepared to go and the environment is established, it’s time to drive them. The tester executes each test using the test cases, contrasting the anticipated outcomes to the real outcomes of each test and identifying it as pass/fail/skip. If the failure occurs, the tester must document what occurred during the test. The tester must also log bugs in the specified bug monitoring system during this process (determined in the test plan phase).
Stage 6:- Bug Fixing
When the testing team finds bugs, they report them to the IT development team. If the project team decides to resolve the bugs, the testing team must retest the programme to ensure that no new bugs were introduced during the patch.
Stage 7:- Closure of the Test Cycle
Test Cycle Closure is the last step of the Software Testing Life Cycle. It entails identifying and assessing cycle termination requirements based on the test scope, performance, cost, time, critical business goals, and software for each representative of the testing team. A review on the testing project/process can be included in this final step of the software testing life cycle. This enables the team to develop and learn in preparation for future research projects.
After meeting the escape requirements and completing the testing process, the test lead issues a test closure study. It is written in a regular format, such as:
- Report on the Tests
- Unique identifier
- Summary of the test
- Variations
- Assessment of Comprehensiveness
- Summary of Findings
- Observation
- Activities Synopsis
- Acceptance
Test Closure Steps
The method of test closure is carried out with the help of six main phases, including :
- Check scheduled Deliverables – The team reviews and analyses the scheduled deliverables that will be given to the project’s stakeholders.
- Close Event Reports – Before the process is completed, the team double-checks that all scheduled deliverables have been delivered and that all incidents have been resolved.
- Handover to Maintenance – After accidents have been resolved and the incident report has been closed, the test-wares are handed over to the maintenance team.
- Full & Archive Testware/Environment – It includes finalising and archiving testware and applications such as test scripts, test environments and test infrastructure among other things.
- Document System Acceptance entails the validation and evaluation of the system in accordance with the strategy described.
- Analyze Best Practices – It identifies the different improvements that will be needed for similar future projects.
Conclusion
The software testing life cycle, in particular, entails the planning, preparation, execution, and reporting of tests. Some phases of the STLC are dependent on others, while others may happen at the same time. You will ensure an efficient and successful testing process by knowing each step of the STLC. The Software Testing Life Cycle is a method for better organizing your testing workflow and bringing consistency to a previously chaotic operation. There are numerous factors to consider during each process, as well as various testing tooling requirements. While preparation is an important part of the process, it does not have to be a time-consuming manual procedure. Software Quality testing companies, such as TestDel, will help you make right and timely decisions. Testing should be prioritized to ensure optimum efficiency. With the aid of TestDel Software Quality Intelligence, you can do just that.
TestDel analyses the applications and gives you the information you need to prioritize testing and create successful testing cycles. You can use TestDel to figure out which tests are essential to improve software quality and which tests are unnecessary and can be skipped.